Nifty reversals are influenced by a combination of technical, fundamental, and macroeconomic factors. Here are the key factors that can lead to a reversal in the Nifty index:
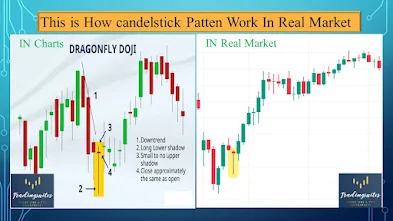 |
| Nifty Reversal Technical Factor Doji Candel |
1. Technical Indicators
- Overbought/Oversold Conditions (RSI, Stochastic): When the Nifty is overbought (RSI > 70) or oversold (RSI < 30), a reversal is likely as traders start taking profits or entering new positions.
- Support and Resistance Levels: Reversal often occurs when the Nifty touches a key support or resistance level and fails to break through.
- Moving Averages (MA, EMA): A crossover of short-term and long-term moving averages, like the 50-day and 200-day MAs, can signal a trend reversal (golden cross or death cross).
- Fibonacci Retracement Levels: Traders often look at Fibonacci levels for potential reversal points, particularly the 38.2%, 50%, and 61.8% levels.
- Candlestick Patterns: Reversal patterns like Doji, Engulfing, or Hammer formations can indicate potential reversals.
2. Market Sentiment
- Investor Sentiment & News Flow: Positive or negative news related to earnings, government policy, global events, or sector-specific updates can change market sentiment and cause Nifty to reverse its trend.
- Fear and Greed Index: Extreme bullish or bearish sentiment can lead to sharp reversals as markets often overreact to emotion-driven trading.
3. Economic Indicators
- Interest Rate Changes: A change in interest rates by the RBI (Reserve Bank of India) can lead to a market reversal, especially if the rate change surprises the market.
- Inflation Data: Higher-than-expected inflation can lead to fears of tighter monetary policy, causing markets to correct.
- GDP Growth and Other Macroeconomic Data: Better-than-expected or worse-than-expected GDP growth can affect market trends.
- Global Cues: U.S. Fed policy, economic data from major economies (US, China, EU), and geopolitical tensions affect investor sentiment and can trigger reversals in the Nifty.
4. Corporate Earnings
- Earnings Surprises: Strong or weak earnings reports, especially from large companies in the Nifty 50, can trigger reversals.
- Guidance and Outlook: Corporate outlooks, particularly if they signal economic slowdown or strong future growth, can change the market’s direction.
5. Foreign Institutional Investors (FII) & Domestic Institutional Investors (DII)
- FII/DII Activity: Heavy buying or selling by FIIs or DIIs can lead to a reversal. For instance, if FIIs start pulling money out of the market, the Nifty can fall.
6. Global Market Trends
- Correlation with U.S. & Asian Markets: Nifty often mirrors global market trends. If global markets, especially the U.S., experience a sharp selloff or rally, Nifty can reverse in the same direction.
- Commodity Prices (Crude Oil, Gold): Rising crude oil prices may lead to a bearish trend due to concerns over inflation and trade deficits, while falling oil prices may provide a boost to the market.
7. Currency Fluctuations
- Rupee-Dollar Exchange Rate: A weakening Indian Rupee can negatively affect companies that rely on imports, while a strengthening Rupee can help them, potentially leading to market reversals.
8. Geopolitical Events
- War, Political Instability, Trade Wars: Any geopolitical events that create uncertainty can trigger market reversals as investors move toward safer assets.
By monitoring these factors, traders can anticipate potential reversals in the Nifty and adjust their strategies accordingly






1 Comments
Good insites
ReplyDelete